Na recent days, East African Community (EAC) don call for swift and coordinated response to contain di ongoing Marburg Virus Disease (MVD) outbreak wey dey happen for Rwanda. Di outbreak, wey Rwanda’s Ministry of Health declare on 27th September 2024, don pose serious threat to regional health security and require urgent action from all EAC Partner States to prevent its spread across borders.
As of 30th September 2024, there be 29 confirmed cases and 10 deaths, with more than 297 contacts under close monitoring. Healthcare workers dey disproportionately affected, and di World Health Organization (WHO) dey worry about di potential regional spread of di disease due to confirmed cases in districts near di borders of Democratic Republic of the Congo (DRC), Uganda, and Tanzania.
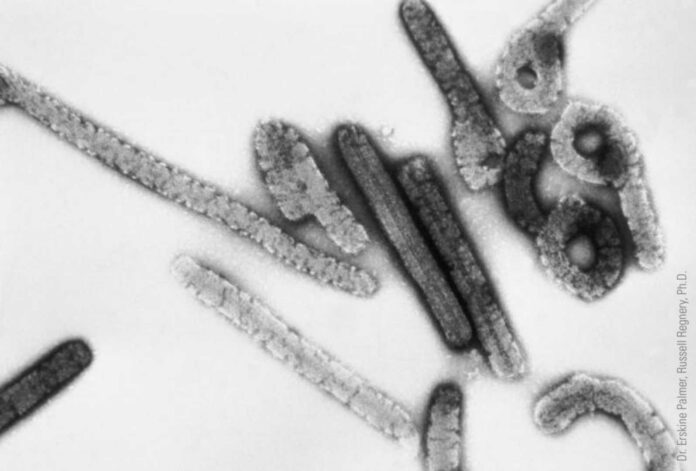
Marburg virus be severe zoonotic disease, similar to Ebola, and e dey associated with high fatality rate wey range from 24% to 88% depending on virus strain and case management. Transmission occur through direct contact with bodily fluids of infected individuals or contaminated surfaces. Since no specific vaccine or treatment dey available, supportive care remain di main form of medical intervention.
EAC Deputy Secretary General, Hon. Andrea Aguer Ariik Malueth, call for Partner States to strengthen their public awareness and infection control protocols, including handwashing, avoiding physical contact with symptomatic individuals, and surveillance at borders and health facilities. Rwanda, wey get robust healthcare infrastructure, dey manage di outbreak with international support, but di scale of di challenge underscore di need for regional collaboration.
Symptoms of Marburg Virus Disease include fever, severe headache, muscle aches and pains, fatigue and weakness, gastrointestinal symptoms like severe diarrhea, abdominal pain, nausea, vomiting, and bleeding from various parts of di body in later stages of di disease. To reduce di risk of contracting Marburg, di public advised to practice proper hand hygiene, avoid contact with fruit bats and their excretions, practice safe burial practices, wear personal protective equipment (PPE) when caring for infected individuals, and avoid contact with nonhuman primates in endemic areas.
Individuals wey suspect say dem may have contracted Marburg should seek medical care immediately, isolate demself to prevent spreading di virus to others, notify local health authorities or go to di nearest healthcare facility for assessment, and avoid contact with others, particularly through bodily fluids, until di suspicion of Marburg infection be ruled out.